- Blogs
- Which Wall Insulation Type Should I Use and What Problems Exist?
Which Wall Insulation Type Should I Use and What Problems Exist?

Wall insulation is one of the most effective ways to improve the energy efficiency and comfort of your home. It can reduce heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, lowering your heating and cooling bills. It can also help to prevent condensation, dampness, and mould growth, which can affect your health and the structural integrity of your home.
But not all walls are the same, and not all types of insulation are suitable for every wall. Depending on the age, design, and construction of your home, you may have different types of walls that require different insulation solutions. In this article, we will explain the main types of walls, the pros and cons of various insulation options, and the issues you may encounter when installing wall insulation.
Types of Walls
The first step to choosing the right type of wall insulation is to identify what kind of walls you have in your home. There are two main categories of walls: cavity walls and solid walls.
Cavity Walls
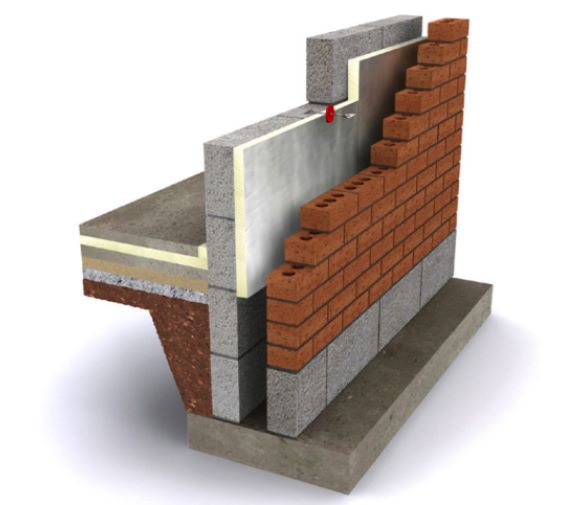 Cavity walls are made up of two layers of brick or blockwork, with a gap or cavity between them. They are common in homes built after the 1920s. The cavity acts as a barrier to prevent moisture from penetrating the inner wall, but it also allows heat to escape easily.
Cavity walls are made up of two layers of brick or blockwork, with a gap or cavity between them. They are common in homes built after the 1920s. The cavity acts as a barrier to prevent moisture from penetrating the inner wall, but it also allows heat to escape easily.
Cavity wall insulation fills the gap between the two layers of the wall with an insulating material, such as mineral wool, polystyrene beads, or foam. This reduces heat loss and improves thermal performance. Cavity wall insulation can be installed by drilling small holes in the outer wall and injecting or blowing the insulation material into the cavity.
The advantages of cavity wall insulation are:
- It is relatively easy and quick to install, with minimal disruption to your home.
- It is usually cheaper than other types of wall insulation.
- It can save you up to £150 per year on your energy bills.
- It can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 610 kg per year.
The disadvantages of cavity wall insulation are:
- It may not be suitable for some types of cavity walls, such as those that are exposed to driving rain, have narrow or uneven cavities, or have damp or damaged bricks or mortar.
- It may require a professional survey and installation by a certified installer.
- It may cause problems with ventilation, drainage, or electrical wiring if not done properly.
- It may reduce the sound insulation of your walls.
Solid Walls
Solid walls are made up of a single layer of brick, stone, concrete, or timber. They are common in homes built before the 1920s. They have no cavity to fill with insulation, so they need to be insulated either from the inside or the outside.
Internal wall insulation involves attaching insulating boards or rolls to the inner surface of the wall or building a stud wall filled with insulation material. This creates a warm and cosy interior, but it also reduces the floor space and changes the appearance of your rooms. Internal wall insulation can be done by yourself or by a professional installer.
The advantages of internal wall insulation are:
- It is cheaper than external wall insulation.
- It can save you up to £455 per year on your energy bills.
- It can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 1,800 kg per year.
- It can improve the sound insulation of your walls.
The disadvantages of internal wall insulation are:
- It can be disruptive and time-consuming to install, as it involves moving furniture, fittings, pipes, and sockets.
- It can affect the character and aesthetics of your home, especially if you have period features or decorative plasterwork.
- It can cause condensation and dampness problems if not done properly, as it reduces the breathability of your walls.
- It can increase the risk of fire if not done properly, as some insulating materials are flammable.
 External wall insulation involves applying an insulating layer and a protective coating to the outer surface of the wall. This creates a weatherproof and attractive exterior, but it also changes the appearance and shape of your home. External wall insulation requires planning permission and professional installation by a certified installer.
External wall insulation involves applying an insulating layer and a protective coating to the outer surface of the wall. This creates a weatherproof and attractive exterior, but it also changes the appearance and shape of your home. External wall insulation requires planning permission and professional installation by a certified installer.
The advantages of external wall insulation are:
- It is more effective than internal wall insulation at reducing heat loss and improving thermal performance.
- It can save you up to £490 per year on your energy bills.
- It can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 1,900 kg per year.
- It can enhance the appearance and value of your home, especially if you have poor-quality or damaged bricks or render.
- It can protect your walls from weathering and decay.
- It can reduce noise pollution from outside.
The disadvantages of external wall insulation are:
- It is more expensive than internal wall insulation.
- It can be difficult and costly to install, as it involves scaffolding, access, and coordination with neighbours and utilities.
- It can affect the character and aesthetics of your home, especially if you have period features or architectural details.
- It can cause problems with ventilation, drainage, or damp proofing if not done properly.
Types of Insulation
The second step to choosing the right type of wall insulation is to compare the different types of insulation materials available. There are many types of insulation, each with its own properties, advantages, and disadvantages. Here are some of the most commonly used types of residential insulation:
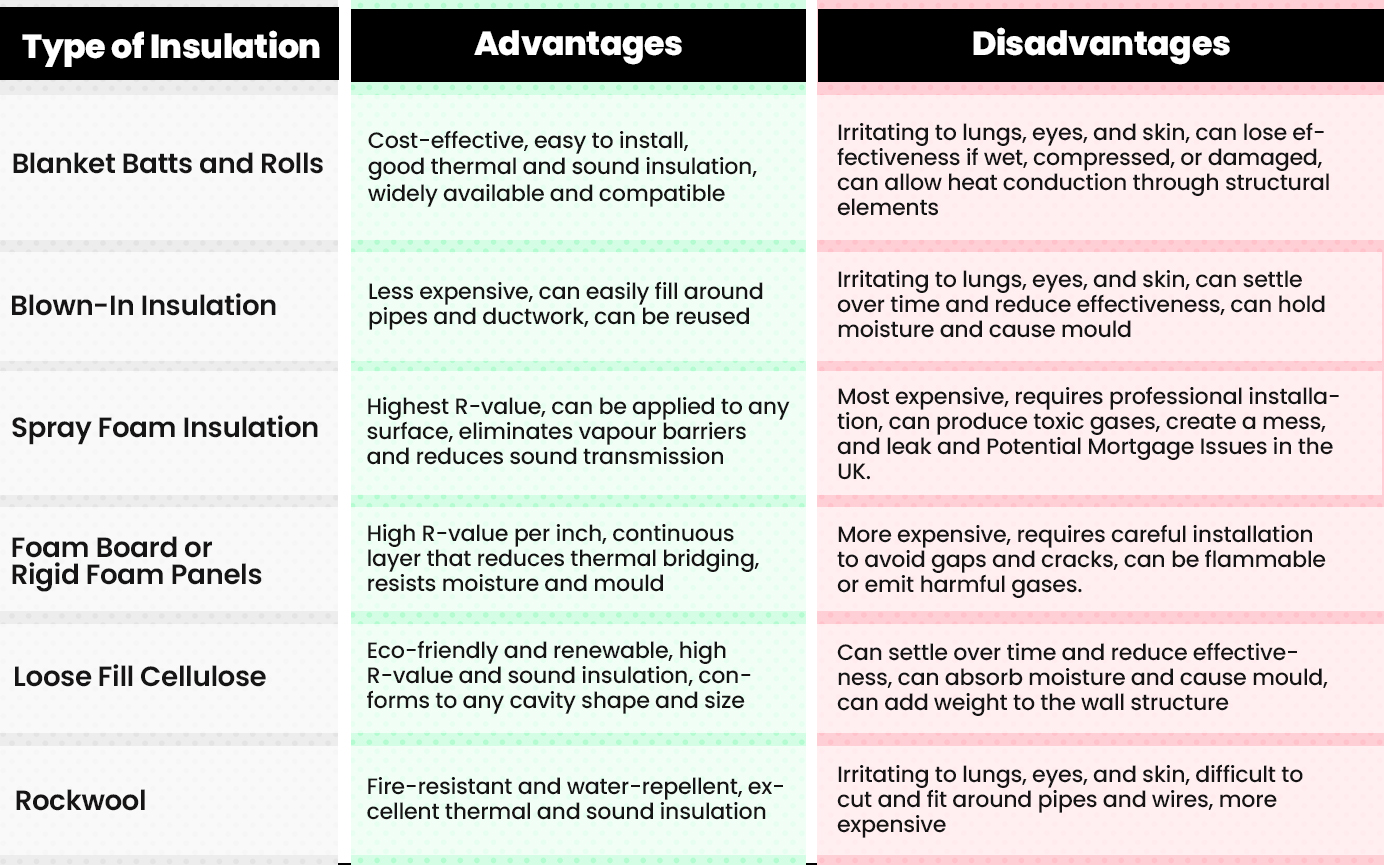
Blanket Batts and Rolls
Blanket batts and rolls are made of fibrous materials, such as fibreglass, mineral wool, cotton, or sheep’s wool. They are pre-cut or rolled into standard sizes and shapes that fit between the studs or joists of a wall. They are suitable for internal wall insulation or for insulating lofts and floors.
The advantages of blanket batts and rolls are:
- They are cost-effective and easy to install.
- They provide good thermal and sound insulation.
- They are widely available and compatible with most types of walls.
The disadvantages of blanket batts and rolls are:
- They can irritate the lungs, eyes, and skin, which can cause health issues.
- They can lose their effectiveness if they get wet, compressed, or damaged.
- They can allow heat conduction through the structural elements of the wall.
Blown-In Insulation
Blown-in insulation is made of small particles of materials, such as cellulose, fibreglass, or mineral wool. It is blown into the cavities or spaces of a wall using a special machine. It is suitable for cavity wall insulation or for insulating hard-to-reach areas.
The advantages of blown-in insulation are:
- It is less expensive than other types of insulation.
- It can easily fill around pipes and ductwork.
- It can be reused by collecting it with a vacuum and relocating it.
The disadvantages of blown-in insulation are:
- It can irritate the lungs, eyes, and skin, which can cause health issues.
- It can settle over time and reduce its effectiveness.
- It can hold moisture and cause problems with performance and mould.
Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation is made of liquid chemicals that expand and harden when sprayed onto a surface. It forms a continuous layer that seals air leaks and gaps. It is suitable for cavity wall insulation or for insulating irregular or complex shapes.
The advantages of spray foam insulation are:
- It has the highest R-value (a measure of thermal resistance) of any type of insulation.
- It can be applied to any surface regardless of location.
- It eliminates the need for separate vapour barriers and reduces sound transmission.
The disadvantages of spray foam insulation are:
- It is the most expensive type of insulation.
- It requires professional installation by a certified installer.
- It can produce toxic gases, create a mess on the site, and leak through unsealed joints and openings.
Foam Board or Rigid Foam Panels
Foam board or rigid foam panels are made of polystyrene, polyurethane or polyisocyanurate. They are cut into thin sheets that can be attached to the surface of a wall. They are suitable for external wall insulation or for insulating basements and foundations.
The advantages of foam board or rigid foam panels are:
- They have a high R-value per inch of thickness.
- They provide a continuous layer that reduces heat loss through thermal bridging.
- They resist moisture and mould growth.
The disadvantages of foam board or rigid foam panels are:
- They are more expensive than other types of insulation.
- They require careful installation to avoid gaps and cracks.
- They can be flammable or emit harmful gases if exposed to fire.
Loose Fill Cellulose
Loose fill cellulose is made of recycled paper that is treated with fire retardants and insecticides. It is blown into the cavities or spaces of a wall using a special machine. It is suitable for cavity wall insulation or for insulating attics and floors.
The advantages of loose fill cellulose are:
- It is an eco-friendly and renewable type of insulation.
- It has a high R-value and provides good sound insulation.
- It conforms to any shape and size of cavity.
The disadvantages of loose fill cellulose are:
- It can settle over time and reduce its effectiveness.
- It can absorb moisture and cause problems with performance and mould.
- It can add weight to the structure of the wall.
Rockwool
Rockwool is made of mineral wool that is spun from molten rock. It is available in batts, rolls, or loose fill forms. It is suitable for internal wall insulation or for insulating lofts and floors.
The advantages of rockwool are:
- It is fire-resistant and does not burn or emit toxic gases.
- It is water-repellent and does not rot or decay.
- It provides excellent thermal and sound insulation.
The disadvantages of rockwool are:
- It can irritate the lungs, eyes, and skin, which can cause health issues.
- It can be difficult to cut and fit around pipes and wires.
- It can be more expensive than other types of insulation.
Comparison Chart for Advantages and Disadvantages for Various Types of Insulation
Issues with Wall Insulation
Installing wall insulation can bring many benefits to your home, but it can also pose some challenges and risks. Here are some of the common issues you may encounter when insulating your walls:
Planning Permission and Building Regulations
Depending on the type and location of your wall insulation, you may need to obtain planning permission and comply with building regulations. This is especially true for external wall insulation, as it can alter the appearance and dimensions of your home. You may also need to consult with your neighbours, landlord, or conservation officer if your home is in a listed building or a conservation area.
Planning permission and building regulations are designed to ensure that your wall insulation is safe, durable, and compatible with the character and environment of your home. They may also require you to meet certain standards of energy efficiency, fire safety, ventilation, and drainage. You should always check with your local authority before starting any wall insulation project.
Cost and Payback Period
The cost of wall insulation depends on many factors, such as the type and size of your walls, the type and amount of insulation material, the method and quality of installation, and the availability of grants or subsidies. The payback period is the time it takes for you to recoup the cost of wall insulation through energy savings.
The cost and payback period of wall insulation vary widely depending on your specific situation. Generally speaking, cavity wall insulation is the cheapest and quickest to pay back, followed by internal wall insulation and external wall insulation. However, you should also consider other factors, such as the comfort, health, and environmental benefits of wall insulation.
Performance and Durability
The performance and durability of wall insulation depend on the quality of the material, installation, and maintenance. Poorly installed or maintained wall insulation can reduce its effectiveness and lifespan. Some of the common problems that can affect the performance and durability of wall insulation are:
- Thermal bridging: This occurs when heat escapes through gaps or cracks in the insulation layer or through structural elements that have lower thermal resistance than the insulation material. Thermal bridging can reduce the R-value of the insulation and cause cold spots on the wall surface.
- Moisture: This occurs when water vapour or liquid water penetrates or accumulates in the insulation layer or on the wall surface. Moisture can reduce the R-value of the insulation, cause mould growth, rotting, corrosion, or structural damage, and create health hazards.
- Air leakage: This occurs when air flows through gaps or cracks in the insulation layer or around windows, doors, pipes, or wires. Air leakage can reduce the R-value of the insulation, increase heat loss or gain, and cause draughts or noise.
To prevent or minimize these problems, you should choose the right type of insulation for your walls, follow the manufacturer’s instructions and best practices for installation, seal all air leaks and gaps around the insulation layer, provide adequate ventilation and drainage for moisture control, and inspect and repair any damage or deterioration regularly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is cavity wall insulation?
A: Cavity wall insulation is a form of insulation that is installed in the gap between the internal and external walls of a property, known as the cavity.
Q: What types of cavity wall insulation are available?
A: There are several types of cavity wall insulation materials available, including mineral wool, polystyrene beads, polyurethane foam, and fibre insulation.
Q: What are the benefits of cavity wall insulation?
A: Cavity wall insulation can help prevent heat from escaping through the walls, which can significantly reduce heating bills and keep your home warm. It can also help prevent damp penetration and damp patches on internal walls.
Q: Does cavity wall insulation cause any problems?
A: While cavity wall insulation can have many benefits, it can also cause problems if not installed correctly. One of the potential issues is damp problems, as insulation can create a barrier that prevents damp from evaporating.
Q: Should I use external or internal wall insulation?
A: The type of insulation you should use depends on the specific requirements of your property. External wall insulation involves insulating the outside of the property, while internal wall insulation is done on the inside. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, so it's essential to consult with a professional to determine which option is best for you.
Q: What are the different types of property insulation available?
A: The different types of property insulation include cavity wall insulation, solid wall insulation, and internal wall insulation. Each type has its own benefits and is suited for different property types.
Q: Are there any building regulations regarding cavity wall insulation?
A: Yes, there are building regulations in place that dictate the standards for cavity wall insulation installation. It's important to ensure that any installation meets these regulations to guarantee proper insulation and compliance with the law.
Q: How long does cavity wall insulation last?
A: Cavity wall insulation can last for many years if installed correctly. Most professional installers offer a guarantee for their work, typically ranging from 25 to 30 years.
Q: Can I retrofit cavity wall insulation to an existing property?
A: Yes, cavity wall insulation can be retrofitted to existing properties. However, it's essential to consult with a professional to assess the feasibility and suitability of the installation for your specific property.
Q: How can I prevent damp issues with cavity wall insulation?
A: There are several steps you can take to help prevent damp issues with cavity wall insulation. These include ensuring proper installation by a reputable installer, addressing any existing damp problems before insulation is installed, and regularly inspecting the property for any signs of damp penetration.
Conclusion
Wall insulation is a smart investment that can improve the energy efficiency and comfort of your home. However, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. You need to consider your specific needs, preferences, budget, and circumstances before choosing the type of wall insulation that suits you best.
You can use online calculators to determine the potential savings and payback duration of various types of wall insulation for your home in order to make an informed choice. A professional installer or energy advisor may evaluate your home's condition and make recommendations for the best solutions for you.
Keep in mind that without the right information, skills, tools, and safety precautions, installing wall insulation is not a project you should attempt on your own. Always work with a professional and trained installer who can ensure high-calibre work and adherence to all applicable laws.

Samuel Hitch
Managing Director
Buy Insulation Online.
Leave A Reply
Your feedback is greatly appreciated, please comment on our content below. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


























































































































































































































































































































































